Using the Arduino
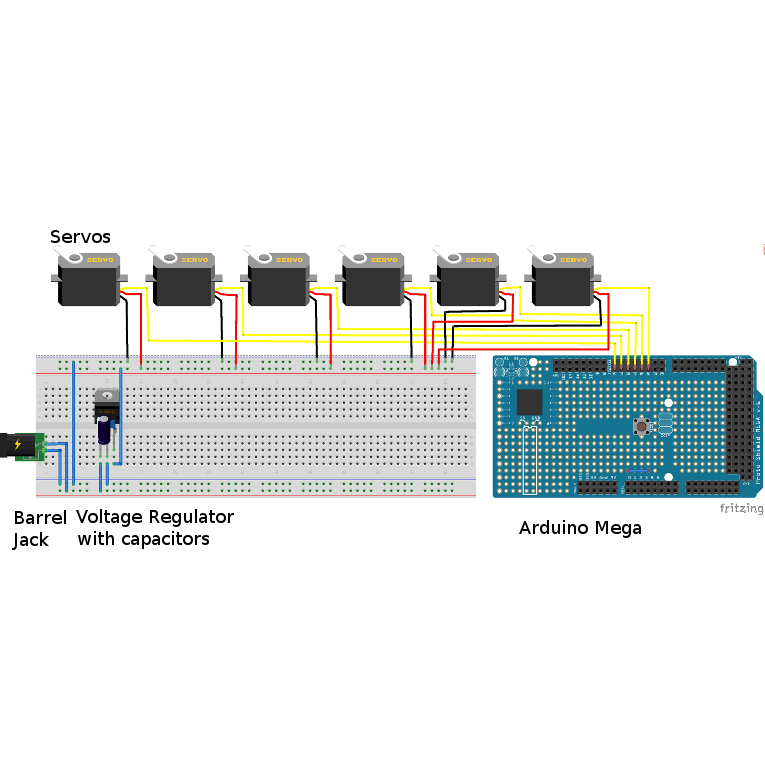
To send the control signals to the motors, we used an Arduino Mega. We chose the Mega because it has more SRAM memory, more EEPROM memory, and more digital output pins than the Arduino Uno we began prototyping with. The Mega is powered via USB, and it provides PWM control signals to each servo.
We found that 36 servos were drawing too much current for the Arduino to power them all from the same rails. We solved this problem by using voltage regulators, which connect to a 9V wall wart and pass 5V into the rails, to power a group of seven or eight servos. The capacitors between the pins of the regulator prevent servo twitching. Calculating how much current our motors draw allowed us to determine that we can power a maximum of eight servos per group. Then, we connected the digital output pins of the Arduino to each motor individually so we were able to use distinct PWM signals to control each servo.
The diagram to the right reflects one of five power groups we created.